In fast-moving teams, flexibility matters more than flashy demos.
This Notion Review looks at real strengths alongside the friction points that slow adoption for many groups. Notion can feel like a blank canvas that morphs into a full workspace once configured correctly.
Early setup rarely feels quick, and certain limitations still push advanced users toward complementary tools.
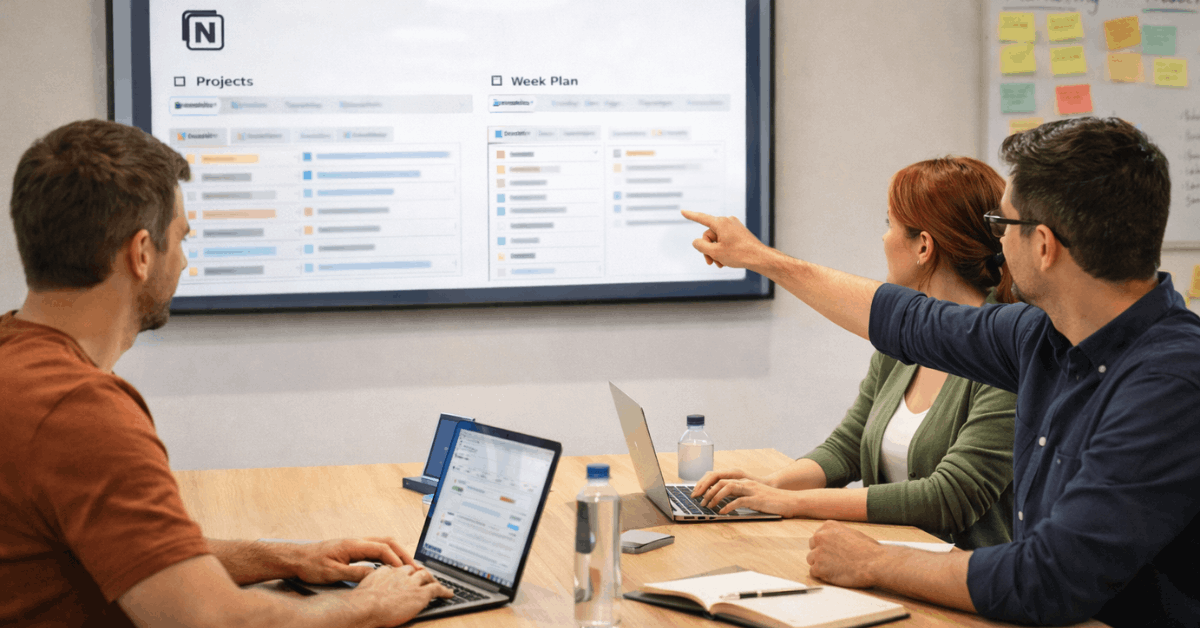

Notion At a Glance
Notion bundles documents, wikis, tasks, and databases in a single, customizable system that adapts to different workflows.
Configuration power sits at the center: properties, relations, rollups, page permissions, and multiple views allow deep tailoring without code. Performance then depends on how cleanly the workspace is modeled and how large the datasets become over time.
What Notion Gets Right
Notion’s strongest advantages show up after a thoughtful build. The points below capture what consistently works well for teams that commit to a structured model.
Versatile Workspace Architecture
Teams stitch together pages, subpages, and databases to create a living system for projects, knowledge, assets, and requests.
Relations and rollups connect tasks to clients, briefs to assets, and notes to decisions, which reduces duplication and context switching. Views such as board, table, calendar, and timeline help different roles see the same data in formats that support their daily work.
Collaboration That Matches Team Habits
Comments, mentions, notifications, and presence cues keep threads attached to the work rather than scattered in separate tools.
Real-time coediting handles docs and specs, while permission groups restrict sensitive pages to the right audiences. Guest sharing supports agencies and contractors without exposing entire workspaces.
Databases Without Database Jargon
Property types cover text, selects, formulas, numbers, dates, people, and files, supporting practical scenarios such as content calendars, CRM-lite pipelines, and sprint boards.
Linked databases surface filtered slices anywhere, so a client page can show only that client’s open tasks, upcoming deadlines, and recent notes in one place.
Continuous Improvements In Visualization
Chart view now turns database results into basic bar, line, pie, and scatter visuals directly in Notion.
Dashboards stay lighter because common summaries no longer require exports. Power users still outgrow the built-in charts for deep analytics, yet quick trend checks finally live inside the workspace.
Where Notion Needs Work
Teams will notice rough edges in several areas. These gaps lead many to add auxiliary tools or limit how much data lands in Notion.
Out-Of-The-Box Readiness
Templates cover common use cases, but robust workspaces still demand upfront modeling. New users often struggle to decide on the right schema for tasks, projects, and documentation.
Early confusion leads to duplicated fields, inconsistent naming, and slow-loading views. Clearer starter blueprints for specific roles would shorten time to value.
Editor Quirks and Pasting Pain
The block editor behaves differently from traditional word processors. Pasting from external sources can introduce odd spacing, misaligned bullets, and inconsistent headings that require cleanup.
Multi-column layouts help complex pages, yet simple list work can feel slower until keyboard habits adapt.
Reporting and Time Measurement
Charts now exist, although reporting remains light compared to dedicated BI or project portfolio tools. Automated timesheets and activity-level time tracking still require templates, buttons, or third-party integrations.
Operational leaders who manage capacity, utilization, and cost recovery typically export data to specialized systems.
Scale and Performance On Large Data
Very large databases can feel sluggish, especially when formulas grow complex or views display many computed columns. Heavy pasting of thousands of rows may stall a page, and broad filters across multiple relations can slow interaction.
Teams mitigate this by splitting mega-tables, trimming properties, and caching focused linked views, yet true scale needs careful design.
Plans and Pricing
The lineup remains straightforward across four tiers that scale with team size and governance needs. Figures below reflect current public information and commonly observed limits for each plan.
Overview Of Tiers:
- The Free plan targets individuals and small tests. A 5 MB per-file upload cap applies, page history stores seven days, and guest sharing is limited. A usage-based team trial is available in shared spaces, helping evaluate collaboration without an immediate payment.
- The Plus plan suits small teams that need fewer constraints. Storage, block counts, and file uploads expand significantly, and page history extends to roughly one month. Guest capacity increases meaningfully for external collaborators.
- The Business plan fits growing organizations that require SAML single sign-on, private teamspaces, longer version history, and richer analytics on page views. Guest allowances scale higher for vendor and client access controlled at the teamspace level.
- The Enterprise plan focuses on security and governance. Admins control sharing defaults, provision users at scale, audit activity, and set fine-grained policies. Dedicated account support helps model structures for multi-division environments.
Notes On Notion AI
Access to Notion AI varies by tier. Functionality now surfaces natively for supported plans, while lower tiers receive limited trial usage. Core use cases include
- summarization,
- rewriting,
- action item extraction, and
- quick drafting inside pages and databases.
Long-form content still benefits from human editing and review, and heavy analytical reporting remains outside AI’s current scope.
Notion Features That Matter Day To Day
Sections below outline practical capabilities and the tradeoffs that surface in real use. Short intros clarify scope, then concrete guidance follows.
Task and Project Views
Teams keep tasks in a database that supports board, table, timeline, and calendar views. Status, assignees, dates, effort, and custom fields combine into role-specific dashboards.
Sprint rituals become smoother when each view stays filtered to current work, blocked items, and upcoming reviews.
Dependencies are modeled through relations and formulas rather than a native dependency engine, which is workable for most teams but less friendly for complex, critical-path planning.
Knowledge and Documentation
Wikis benefit from nested pages, backlinks, and simple formatting. Cross-linking specs, product decisions, and runbooks builds clarity across teams.
Reviewers want to change visibility, so page history and comments serve as the lightweight audit trail. Governance improves when admins standardize naming patterns and use templates for repeatable sections like PRDs or SOPs.
Databases and Relations
Practical modeling tips help maintain speed. Narrow each table’s purpose, avoid storing unrelated data in a single mega-table, and keep formulas lean. Linked views should focus on small filtered slices rather than full tables.
Rollups can summarize counts, totals, and latest dates, although heavy nesting across multiple relations may slow rendering.
Charts and Light Analytics
Chart view now supports quick visuals for team standups and stakeholder updates. Simple KPI tiles and trend snapshots reduce exports for basic reporting. Robust dashboards that require drill-downs, multi-table joins, or cohort analysis still belong in specialized tools.
A reliable path is to pipe selected Notion data into a BI platform for monthly and quarterly reviews.
Who Should Use Notion
Notion serves best when teams value modeling freedom and can invest time to build a consistent structure.
Agencies, content operations, and product squads that combine documentation, tasks, and assets in one system see the most benefit.
Organizations that require out-of-the-box enterprise reporting, advanced resource management, or formal time capture will likely supplement Notion or choose a platform centered on those needs.
Set Up Recommendations That Prevent Problems
Clear structure makes or breaks long-term success. The steps here reduce clutter and improve speed without adding complexity.
- Define a minimal data model for each area, such as tasks, content, clients, and assets. Keep property names short and consistent across databases.
- Create opinionated templates that prefill statuses, owners, and sections for common work types. Standardization stops schema drift.
- Limit any one database view to what a role needs for the next two weeks. Broad, unfiltered views slow down and confuse users.
- Centralize key relations instead of duplicating fields in multiple tables. Use rollups for counts and last-updated dates instead of formula chains.
- Establish permission groups early. Map groups to teamspaces and default new pages to the least permissive sensible setting.
Notion Alternatives Worth Considering
A quick scan of known options helps match priorities to platform strengths. Monday.com emphasizes visual boards, templates, and automations across teams that want structured start-up speed.
ClickUp offers traditional project management patterns, broad feature coverage, and strong list and board execution for squads that prefer familiar flows.
Smartsheet combines grid-first work management with enterprise-grade automations and sheet-based modeling suited to PMO-style governance.
Last Thought
Notion handles documents, tasks, and lightweight databases in one place, which reduces the tool sprawl that slows many teams.
Friction appears during initial modeling, heavy pasting, large datasets, and formal reporting.
Successful rollouts set narrow goals, keep schemas clean, and integrate external analytics where deep measurement matters. Careful structure turns Notion into a reliable system of record for everyday work.