In fast production cycles, a clear Descript overview helps decide whether the tool fits everyday editing. Text-first controls turn spoken audio into editable text, then map changes back onto the media.
Editors reported meaningful time savings on dialogue-heavy projects, especially podcasts and tutorials. Teams valued collaboration that feels closer to a document than a traditional timeline.
Because transcript-first editing changes how you work, expectations matter. Strong results appear when projects center on interviews, screen recordings, and hosted explainers. Advanced color, motion, and complex mixes remain better suited to pro NLEs.
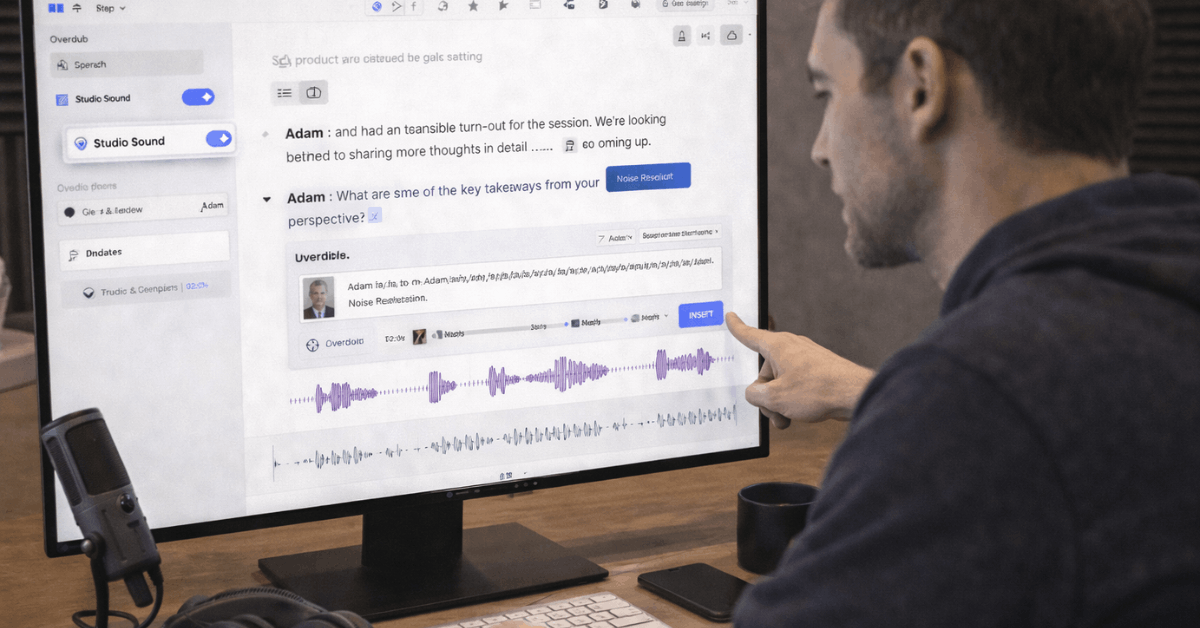
What Descript Is and Who It Helps
As an all-in-one editor, Descript supports recording, transcription, rough cuts, and quick output for social formats.
Text-based editing removes heavy timeline work for creators focused on talking content rather than cinematic polish. Podcasters, course makers, marketers, and solo producers gain the most because frequent retakes and filler trims consume time elsewhere.
Across tests, the platform’s core advantage came from intuitive transcript editing. Edits in text ripple through the audio and video, which makes repetitive cleanup faster. AI features can accelerate, though oversight remains essential for accuracy and tone.
What We Liked Most After Testing
Helpful context strengthens this section because several features work best together. Editors who plan transcripts, pause points, and segment markers realize larger gains.
Beginners appreciate an interface that behaves like a document instead of a dense timeline. Teams collaborate in real time without shuffling project files.
Text-Based Editing
Directly editing the transcript to cut stumbles, reorder beats, or remove tangents shortens rough-cut time significantly. For long interviews, selective paragraph trims feel natural and readable. Scene changes follow the text, so a single pass can reshape an entire episode.
AI-Powered Time Savers
Descript Studio Sound improves noisy recordings by reducing hiss and room echo in a click. Descript filler word removal targets uhs, ums, and similar crutches, then proposes safe deletions. These actions reduce manual razor work that usually clutters early passes.
Overdub For Patch Fixes
Descript Overdub allows quick corrections without re-recording full segments. Short inserts cover missed words, date fixes, or disclaimers and keep cadence intact. Longer reads remain less convincing, so reserved use on small pickups works best.
Collaboration That Works Like Documents
Live comments, shared links, and permissions streamline review cycles for distributed teams. Stakeholders scan transcripts, suggest trims, and approve language without learning an editing timeline. Project momentum improves because feedback applies directly where words live.
Workflow Efficiency That Scales
Producers reported doubling output on dialogue shows once muscle memory formed. Template projects for intros, lower thirds, and social clips reduce recurring setup overhead. Export presets for 4K or platform-specific sizes ensure predictable delivery.
Descript AI Action Tools: Realistic Expectations
Clear expectations avoid disappointment because automation still needs editing judgment. These features generate summaries, show notes, scripts, and social snippets from source audio.
Initial drafts land quickly, then benefit from factual checks and tone polish. Treat them like a junior assistant who needs strong direction.
- Podcast Show Notes Generator: Produces a clean structure, although terminology and names sometimes require corrections for specialized topics.
- Podcast Summary Generator: Captures themes in short form, yet can miss nuance on complex discussions or multi-guest debates.
- Social Media Post Generator: Generates usable hooks intermittently; best results come after prompts specify voice, audience, and length.
- Script and Article Writer: Speeds first drafts on general topics; niche subjects still need expert input and additional sourcing.
Transcription Quality and Editing Flow
Accuracy varies with accent diversity, microphone quality, and speech pace. Clean, close-miked tracks transcribe well and reduce correction time; cross-talk and fast interruptions degrade results.
Editors found that a brief pre-flight checklist for mic placement, room treatment, and speaker pacing lifts accuracy before transcription even begins.
Editing inside the transcript feels natural once habits form. Selecting a sentence to remove an anecdote or tightening pauses feels like document editing. Export options cover common repurposing formats, though occasional compatibility checks are helpful when pushing text into caption tools or CMS fields.
Overdub and Studio Sound In Practice
Short Overdub inserts handle names, numbers, and single-sentence fixes without scheduling new sessions. Consistency improves when training data matches the microphone and environment used in the episode.
Longer passages still reveal synthetic edges, so producers reserve the feature for micro edits. Studio Sound helps rescue remote interviews, webinars, and on-site audio recorded in reflective rooms.
Results vary by source quality; heavy background noise or clipping cannot be fully repaired. A sensible approach applies moderate enhancement rather than aggressive settings that introduce artifacts.
Collaboration and Workflow Gains
Teams share projects like documents, add comments at exact transcript positions, and track approvals. Producers create review cuts faster because stakeholders highlight text instead of timecodes.
Remote contributors record within the same ecosystem, which simplifies asset management while keeping version history intact.
Template libraries earn their keep during recurring series. Consistent openers, music beds, and lower third styles stay organized for weekly outputs. Social repackaging also benefits because highlight reels and audiograms start from the transcript, not a blank timeline.
Pricing and Plans Snapshot
Pricing influences adoption, especially when transcription hours drive monthly costs. Current tiers usually span Free, Creator, Pro, and Enterprise. Usage patterns matter more than headline price because hour caps and storage shape feasibility.
| Plan | Core Inclusions |
| Descript Free | About 1 hour each of transcription and remote recording, 720p export, limited storage. |
| Descript Creator | Around 10 hours each of transcription and remote recording, 4K export, larger storage allocation. |
| Descript Pro | Around 30 hours each, unlimited exports, advanced effects, expanded cloud storage. |
| Descript Enterprise | Custom limits, admin controls, SSO, support, and security reviews for larger teams. |
Cost effectiveness depends on episode length, release frequency, and multi-seat needs. Teams that publish weekly interviews often land on Creator or Pro to avoid mid-month caps.

Drawbacks Reported By Real Users
Trade-offs matter because a tool’s speed does not eliminate other gaps. Plan rollouts and frequent updates sometimes shift menus and controls. Editors handling complex audio stacks still migrate to a pro DAW for finishing.
- Learning Curve: New users report time spent adapting to a transcript-first mindset and hidden power features.
- Transcription For Accents: Accuracy dips with diverse accents and rapid cross-talk, increasing manual corrections.
- Interface and File Management: Large, multi-episode workspaces feel cluttered until conventions and folders are enforced.
- Frequent Updates: Feature relocations interrupt habits and slow teams until new muscle memory forms.
- Bugs and Support: Occasional glitches and slower ticket responses disrupt tight delivery windows.
Who Should Choose Descript, Who Should Skip
For interview-driven podcasts, webinar edits, tutorials, and screen-recorded courses, Descript accelerates rough cuts and routine cleanup. Editors working under deadlines gain the most when filler removal, Studio Sound, and transcript edits clear hours of timeline work.
Teams that live in shared documents onboard quickly and collaborate without exporting project archives. Complex documentary mixes, music-heavy storytelling, and color-critical video productions remain better in dedicated DAWs and NLEs.
Multitrack music editing, surgical noise repair, and advanced grading exceed the intended scope. A hybrid workflow often wins: assemble and clean in Descript, finish in a specialist tool.
Alternatives and When To Switch
Content repurposing specialists may prefer a generator that prioritizes blog drafts, social captions, reels, and SEO metadata. Several services market end-to-end repackaging centered on a single uploaded episode.
One notable option focuses on automated show notes, chapters, reels, audiograms, and long-form articles, then layers editor tools for refinement. Pricing on such platforms typically ranges from a no-cost tier for trial workloads to mid-tier plans that add in-app editing and assistant features.
Higher tiers add instant reels, audiogram automation, and larger monthly allowances for active studios. Selection should follow your publishing cadence, volume of assets per episode, and desired control over brand voice.
Last Thoughts
Strong results for dialogue-based media make Descript a practical choice for many teams. Text-based editing, Descript Studio Sound, Descript Overdub, and real-time collaboration streamline the path from raw tape to publishable cut.
AI drafting helps kickstart notes and summaries, although expert review remains essential for accuracy and nuance. For podcast producers who value speed to first cut, the platform earns a place in the stack.
For advanced sound design or complex video finishing, pairing Descript with a pro editor keeps the quality high. Sensible adoption starts small on one show, collects timing data, and then scales licenses if the gains prove repeatable.