In high-traffic hours, the reliability of using Slack matters more than features. Daily volume is immense, and that scale shows up during Monday mornings, product launches, and incident bridges.
Messages top hundreds of millions per day, and workflows fire constantly, so your plan for resilience needs to live inside Slack rather than around it.
What Reliability Means In Slack
Reliability covers a few practical signals that teams actually feel. Uptime is the first layer, but peak-hour performance also depends on message delivery latency, notification accuracy, search freshness, file preview speed, and the stability of calls or huddles.
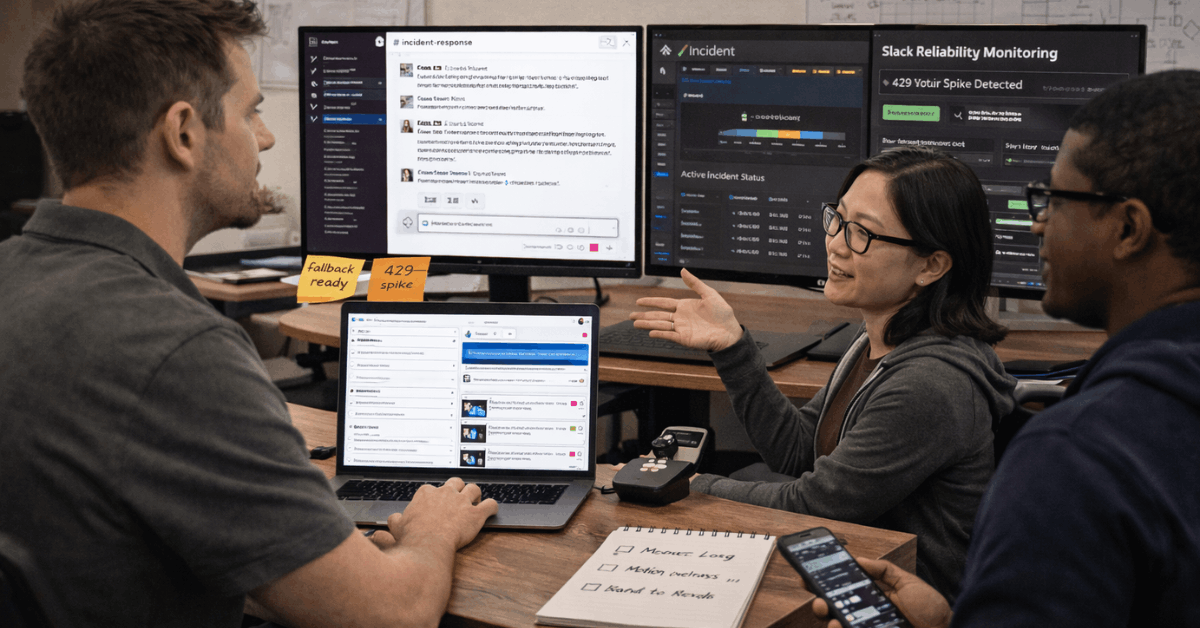
Service feels reliable when each layer remains responsive while usage spikes, not only when the service is technically available.
Expect variance across devices and networks, especially on older desktop clients or constrained mobile connections. Healthy workspaces pair platform assurances with local safeguards such as OS updates, network QoS, and a short list of approved extensions.
Slack’s Promises and Recent History
Teams should anchor expectations to what Slack commits publicly, then adjust for real-world incidents. Enterprise plans advertise a 99.99 percent availability target backed by credits, which translates to roughly 4.3 minutes of monthly downtime at most.
Status calendars and post-mortems show that issues still surface during busy periods, including notification delays and intermittent message send failures. Peaks magnify small regressions, so design operations around occasional turbulence rather than assuming perfect uptime.
Recent Incidents At A Glance
A brief snapshot helps set expectations for incident types felt during peaks.
| Date (UTC) | Area Affected | User Impact Summary | Typical Workarounds |
| 2025-01-27 | Notifications, threads | Delayed notifications and difficulty locating threads | DM for critical updates, channel mentions |
| 2025-02-26 | Login, messaging, workflows | Trouble logging in and sending messages for several hours | Email or phone for P0, local runbooks |
| 2025-06-01 to 2025-06-05 | Connectivity, org dashboards | Trouble connecting and loading, sporadic send/receive issues | Refresh client, web fallback, status checks |
Incidents vary by region and client version, and the Slack status page remains the source of truth for unfolding events.
Where Peak Use Bends The Experience
Teams describe a common pattern during spikes: conversations fragment, alerts pile up, and context recovery takes longer than planned. A Remote Clan poll cited a majority of members running Slack daily, then several contributors raised the same pain points.
Interruptions felt frequent, notification rules required agreements, and reconstructing long threads cost real time.
One team lead argued that Slack excels at short messages and brainstorms, but deeper decisions still belong in meetings or long-form documents. Others set expectations that Slack communication is asynchronous, reserving synchronous outreach for true urgency.
Slacks Reliability
When notifications misfire or latency creeps up, people over-ping colleagues or switch channels, which increases noise and hides important updates.
When search indexing lags, channel history becomes harder to mine, which slows onboarding and incident handoffs. Reliability, in practice, blends platform stability with cultural guardrails that prevent noise from crowding the signal.
Capacity, Limits, and What They Mean At Scale
Large deployments lean on Enterprise Grid and its guardrails to manage concurrency, compliance, and security boundaries. Enterprise grid reliability depends on more than raw uptime; SSO health, mobile device policies, and network egress rules all contribute to perceived stability.
Data residency regions also matter for latency and regulation. Placing workspaces in the closest available region can cut search and file preview delays during traffic spikes, particularly for globally distributed teams.
APIs and Integrations
App-posted messages, workflow steps, and bot actions are subject to Slack’s API rate limits, which become visible when a campaign or incident page pushes automated updates to large audiences.
Queueing, exponential backoff, and batching keep integrations healthy when traffic surges and prevent “429 Too Many Requests” failures from cascading through channels where stakeholders expect minute-by-minute updates.
AI And Privacy Signals That Affect Reliability
Slack AI adds summaries, daily recaps, and enhanced search, which improves catch-up speed after peaks. Design choices also matter for trust. Customer data is not used to train third-party models, and Slack hosts models within its infrastructure to limit data exposure.
Recent policy changes around how third-party tools can index Slack data also reinforce controls. Operationally, those boundaries reduce integration risk during busy periods, since fewer external services cache long-term message data outside agreed scopes.
Practical Reliability Scorecard
Treat performance like any production system. Measure a handful of user-visible metrics, set thresholds, then review weekly. Keep targets conservative during known spikes, like Mondays at 9 a.m. local time or the first hour after all-hands.
Five Metrics To Track And Where To Read Them
| Metric | Target During Peaks | Where To Check | What It Tells You |
| Message round-trip time | Under 2 seconds median | Client tests, channel timestamps | End-user send and receive latency |
| Notification delivery variance | Under 10 seconds | Test channel, device mix | Mobile vs desktop reliability gap |
| Search freshness lag | Under 2 minutes | Known phrase re-index test | Indexing speed under load |
| Workflow execution time | Under 60 seconds per step | Workflow run history | Automation backlog risk |
| Huddles connection failure rate | Under 2 percent | Network logs, user reports | Real-time media stability |
Targets should be tightened progressively. Start at conservative thresholds, then ratchet as confidence grows.
Operational Playbook For Peak-Hour Performance
Planning turns peaks into routine. The steps below concentrate on outcomes that end users feel immediately and keep the signal flowing even when parts of the stack wobble.
- Establish a single reliability channel for status, runbooks, and verified updates. Keep noise low and require owners for each pinned checklist.
- Adopt a simple live-ops rubric for incidents: detect, declare, direct, deliver, and debrief. Publish owner handoffs visibly to reduce duplicate pings.
- Tune integrations for resilience with queues, retries, and backoff. Treat API rate limits in Slack as guardrails and alert on 429 spikes.
- Calibrate notification expectations in writing. Encourage mentions sparingly, use channel-wide highlights for P0 only, and normalize async replies outside emergencies.
- Rehearse web fallback and mobile failover. If desktop clients stall, switch to the browser, refresh tokens, and continue work while desktop repairs sync.
Department-Level Notes That Influence Reliability
Sales teams depend on fast search and CRM alerts inside channels, so pipeline rooms should pin a short status note during incidents and route urgent approvals to email or CRM tasks temporarily.
Service teams lean on tierless support patterns, which depend on consistent notifications and clear case transfers; when notifications degrade, run a manual sweep of the queue every fifteen minutes.
Marketing teams depend on workflow approvals; configure an emergency form that auto-assigns approvers if a workflow exceeds 1 minute. Finance teams rely on time-bound approvals; mirror requests to a backup channel, and archive duplicates after recovery. IT teams own the backbone; publish a two-line status header visible to all employees so people stop guessing what is broken.
Security, Compliance, and Their Reliability Side Effects
Security events and compliance tasks often arrive during peak hours. Enterprise encryption, audit controls, and granular retention policies keep work on track while investigations proceed.
Data residency regions support local regulations and can marginally reduce latency in far-flung offices. Strong baseline hygiene remains decisive: enforce SSO, rotate tokens, audit high-volume bots each quarter, and cap privileged scopes.
Reliability improves when fragile apps are retired and critical ones adopt least-privilege designs.
Handling Human Factors That Hurt Reliability
People generate load. High-stakes launches create overlapping pings, and incident rooms can spiral into noise. Short norms help. Ask teams to front-load decisions in channel topics or canvases, keep one canonical thread per decision, and summarize outcomes into canvases or docs within an hour.
When brainstorming in fast chat, move complex ideas to a longer note or a quick call, then capture the decision. That practice reduces rework and lowers the cost of catching up after outages or notification delays.
Verdict: Reliable Enough For Peaks, If You Operate It Deliberately
Across busy organizations, Slack holds up during peaks when teams treat reliability as an operating discipline.
Platform commitments such as the Slack uptime SLA and the visible Slack status page provide the backbone, while real-world incidents remind everyone to keep playbooks sharp.
The combination of cultural norms, sane integration design, and light live-ops turns a chat platform into a dependable work platform, even in the heaviest hours.